Azure provides a wide array of services, each with its own pricing model. Conducting detailed cost analysis helps organizations understand where their money is being spent within Azure. It allows them to identify areas of overspending or underutilization and optimize their resources accordingly.
By analysing costs, organizations can identify unused or underutilized resources and either scale them down or decommission them altogether. This optimization ensures that resources are allocated efficiently, reducing unnecessary expenses.
Understanding the cost implications of using various Azure services helps organizations plan their budgets more accurately. Detailed cost analysis enables them to forecast expenses, allocate funds appropriately, and avoid unexpected cost overruns.
Turbo360 Azure Cost Analyzer comes in the first place providing this detailed cost analysis for the Azure environment. The cost can be obtained at very granular level based on subscriptions, resource groups, types, service names and much more.
With this detailed cost, the customers/organization often get the complete cost spent on their Azure resources ensuring transparency and compliance in resource usage. It is a critical component of effective cloud cost management and governance strategies. Let’s deep dive into how the detailed analysis is done with Turbo360.
Turbo360 Azure Cost Management Tool
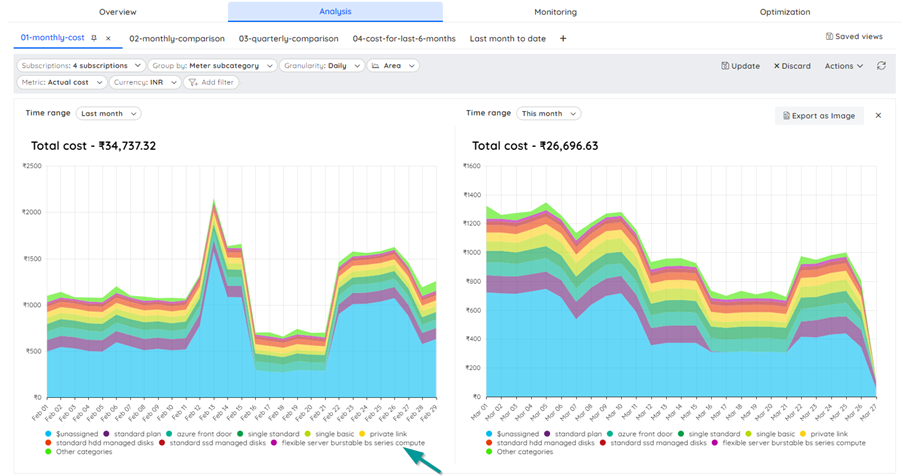
Turbo360 Cost Analyzer provides the analysis view which contains multiple filter options with which the cost data can be seen. These views can be saved for future use so that the users need not come and apply the filters once again to view the data. This view can once again be drilled down with the different filter options available.
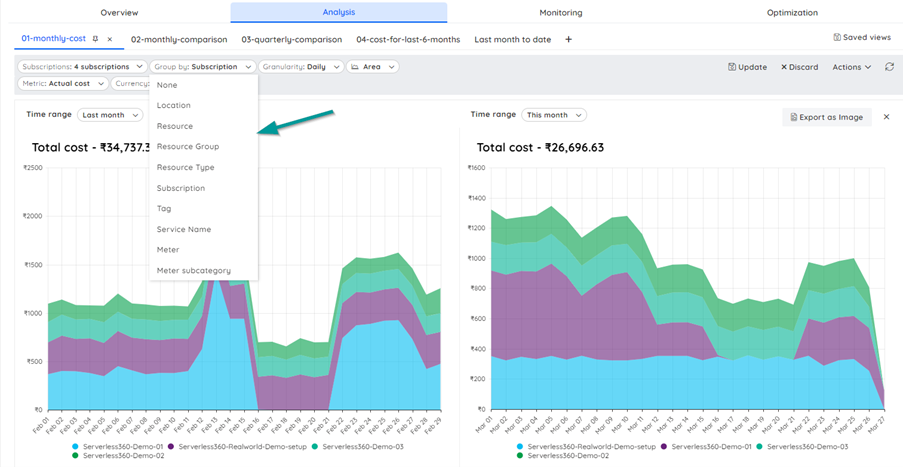
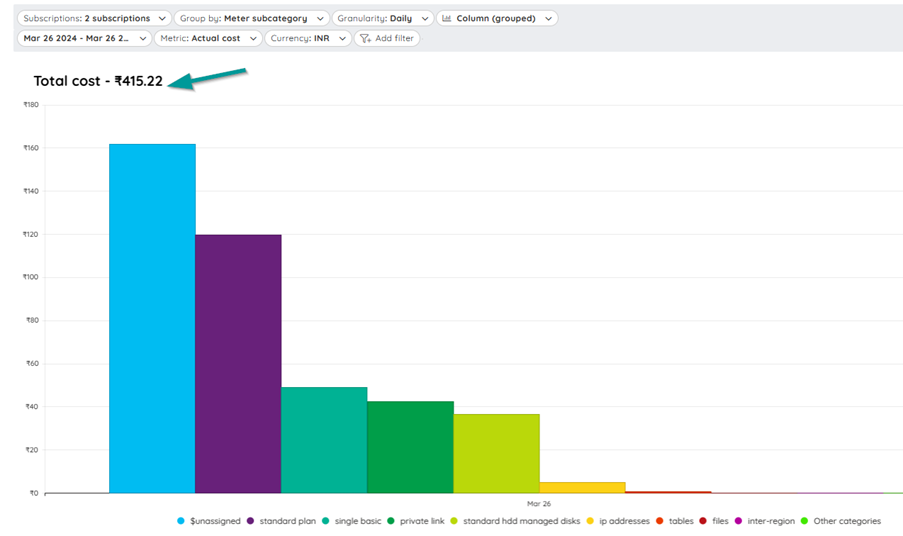
Even though there are different filter options like the Resource group, resource type, location which are self-explanatory the two important filter options draw the users’ attention – the service name and the meter.
Azure services
A service can be considered as a collection of features and capabilities that you can use to build and manage your applications. These services support various business use cases, enabling organizations to innovate, scale, and secure their applications and data. Some of the important Azure services include:
Azure Compute Services
They help the organizations to deploy, manage and scale applications and workloads in the cloud – App service, Azure Functions, Containers, Virtual Machines
Azure Storage services
They provide scalable and secure storage options which include – Azure Data Lake Storage, HPC cache, Managed Disks.
Usecase video on “Spike in Azure storage costs – Monitoring and troubleshooting”
Azure Database services
They provide managed databases to simplify the deployment, management, and scaling of databases in the cloud which include – Apache Cassandra MI, Azure Cosmo DB, Redis Cache, Azure Database for MySQL.
Azure Networking services
They provide networking solutions for organizations to build, manage, and secure their network infrastructure in the Azure cloud environment – Application gateway, Azure DNS, Private link.
With these wide range of services available, the resources can be scaled up or down based on the requirements as per the varying workloads and traffic. Since the services provide a cost effective pay-as-you-go model, it helps the organizations to optimize costs based on the actual usage.
When the cost analysis is done at the resource type level, we can get the cost incurred by each resource. But at the service level we can get the cost of the individual services together.
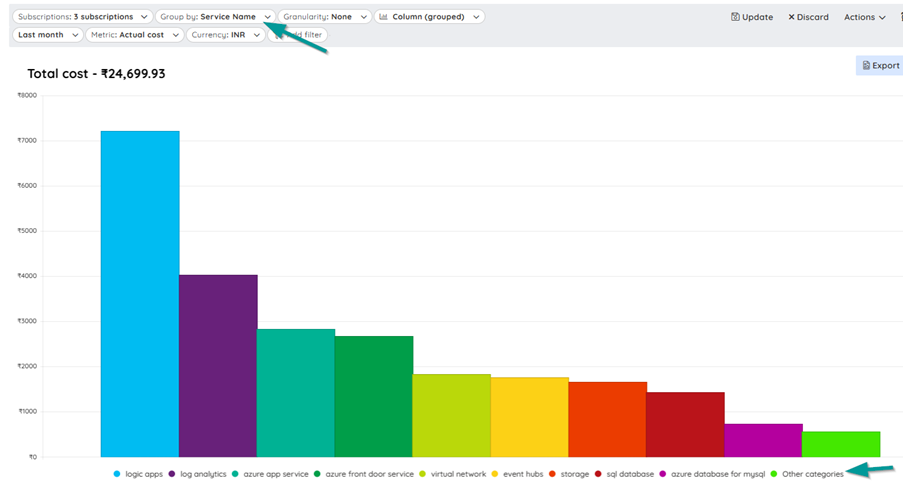
The Meter and Meter sub-category
The meter and the meter subcategory refer to the service tiers with which the resources would be deployed in Azure. Meters are used to track a resource’s usage throughout its lifetime. For example, let us consider creating a Virtual machine. The VM would have the following meters for which the billing will be considered.
- Compute hours
- Data Transfer In
- Data Transfer Out
- Standard IO Disk
- Standard Managed Disk and much more
Similarly, there are different metrics available for each of the resource.
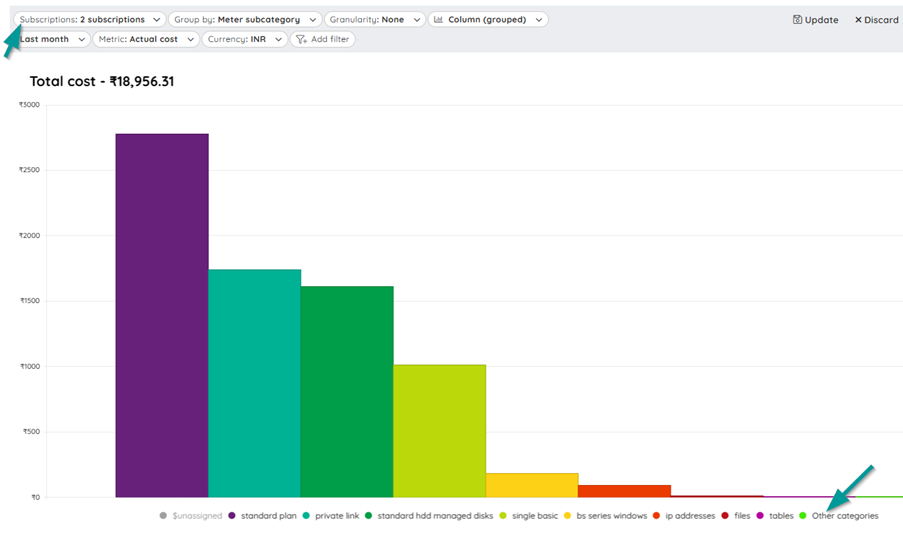
The meter subcategory on the other hand would be the subgroup of any of the resource. For a storage account, the subcategory would be tables, files, queues. For a database service, it would be a SQL database and for the storage, it would drill down to queues and tables.
When the cost analysis is done at the meter subcategory level, this will provide more details on to which categories incur more cost at a deeper level.
In the Azure portal, the cost analysis can be done only by using the different filter options available in the analysis section. But with Turbo360 Cost Analysis, the user can drill down to each level starting from subscription to resource group, resource, service name and the meter subcategory. This way the FinOps team can get the complete cost on a level-by-level basis. Consider for a subscription, if we want to know for which service -> meter -> meter subcategory, the cost is high, we can drill down in the analysis view from Turbo360 which is not available with the Azure portal. For a storage account, we can check which of the tables/queues have high cost.
Why Service names and meter are important in cost analysis?
While there are different categories to look out in the cost Azure analysis, the service names and the meter options play an important role. Rather than checking for the individual resources, we can check for the complete group which incurs more cost. For an organization with different departments, this report would be very helpful.
The FinOps team can identify the services with high cost and special attention can be given to any unexpected spikes in spending or services that consistently incur high costs. They examine the usage patterns associated with each service and look for any instances of underutilized resources or services that could be downsized or optimized.
The team can also compare costs across different projects or departments within the organization. This helps identify areas where costs may be disproportionately allocated or where cost-saving measures can be implemented.
Based on their analysis, the team generates reports summarizing the findings and recommendations for optimizing Azure spending. These reports may include actionable insights, such as rightsizing virtual machines, leveraging reserved instances, or adopting serverless computing where applicable. The recommendations can be obtained from the Turbo360 Cost Optimization feature.
Finally, they can set up regular monitoring of Azure costs and trends over time. This ongoing analysis ensures that cost optimization efforts remain effective, and adjustments can be made as needed.
New in Turbo360: Resource-Level Utilization Insights
Turbo360’s Azure Cost Analysis feature just got more powerful. Now, when you click on any resource, you’ll see detailed utilization metrics and cost trends from the past 30 days.
Get a clear view of:
- Daily spend patterns to spot anomalies or spikes
- Meter-level cost breakdown (compute, storage, data transfer, etc.)
- The exact operations driving your cloud costs
This helps teams go beyond surface-level cost analysis and pinpoint real optimization opportunities—all in one view.
Turbo360 Monitoring
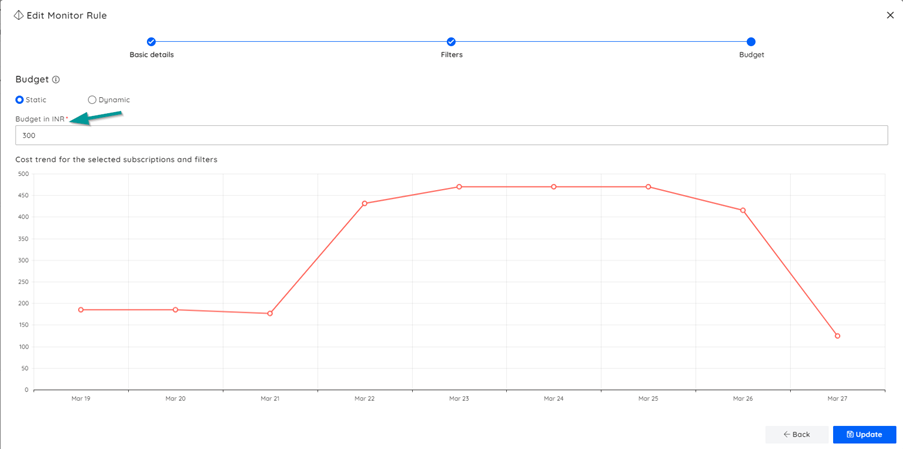
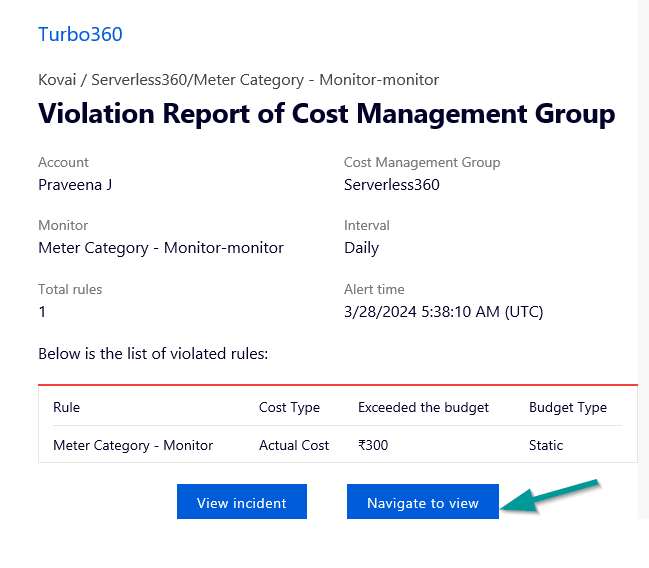
The above-mentioned Analysis views can be monitored, and the users can be notified when the budget values cross the configured threshold values. The monitoring is very easy to setup with just few clicks.
Conclusion
Hence with Turbo360, the organizations can effectively analyse the Azure costs based on the service names, identify opportunities for optimization and implement measures to ensure efficient utilization of resources while maximizing cost savings. Get 14-day free trial today to discover the potential savings in your environment.